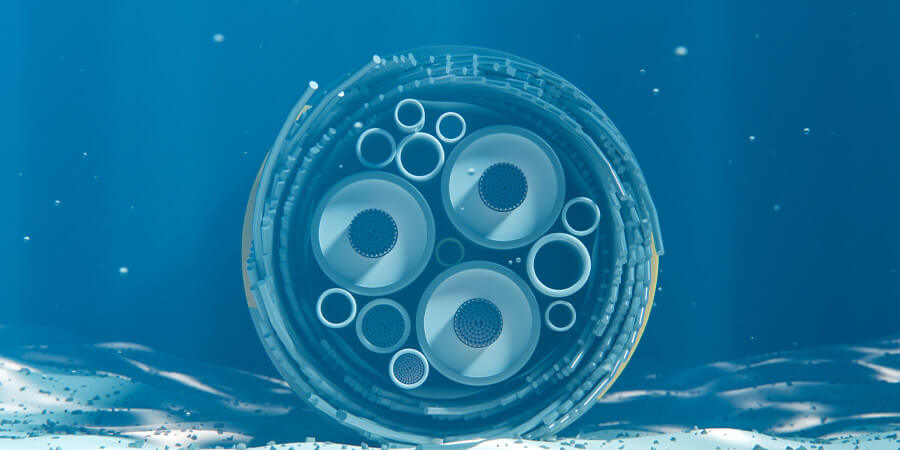
As Africa continues to embrace the digital revolution, the reliance on global digital infrastructure has grown immensely. The continent's digital future depends heavily on powerful and resilient connectivity solutions, with submarine cables playing a crucial role in this transformation. These cables, which run beneath the oceans to link continents, are the lifeblood of modern communications, enabling high-speed internet, voice, and data exchanges between Africa and the rest of the world. Ensuring the resilience of these cables is now more critical than ever, as the continent seeks to enhance its digital economy, promote innovation, and improve access to essential services such as healthcare, education, and finance.
The Role of Submarine Cables in Africa’s Digital Connectivity
Submarine cables are the backbone of global telecommunications, transmitting approximately 99% of international data traffic. In Africa, these cables connect the continent to the rest of the world, facilitating communication, e-commerce, and digital services. Without them, the growth of the African digital economy would be stunted, and access to vital resources such as remote healthcare or online education would remain limited.
Historically, Africa has faced significant challenges in terms of digital connectivity. Many countries were isolated from global communication networks, relying on costly satellite links that were often unreliable and offered lower speeds. However, with the advent of new submarine cables, such as the Africa Coast to Europe (ACE) cable, the East African Submarine Cable System (EASSy), and the South Atlantic Cable System (SACS), Africa has seen a dramatic improvement in its international internet connectivity. These cables have lowered costs, improved bandwidth, and made it possible for Africa’s tech ecosystem to flourish.
Submarine cables provide faster, more reliable, and cost-effective internet connectivity compared to satellite communication, which has higher latency and limited bandwidth. The introduction of these cables has led to an increase in data availability, enabling businesses, governments, and individuals to access digital tools and services that were once out of reach. The resulting digital transformation is facilitating economic growth, job creation, and improving the quality of life across the continent.
Challenges to Submarine Cable Resilience in Africa
Despite the significant benefits, Africa’s resilient submarine cable infrastructure faces several challenges. Physical vulnerability of these cables is a major issue. Submarine cables, which are typically laid on the ocean floor, are prone to damage from various factors, including natural events like earthquakes and undersea landslides, as well as human activities such as fishing, anchoring, and shipping traffic. While cables are designed with protective layers, disruptions remain a possibility, and damage to cables can result in significant service outages, affecting entire regions.
For example, in 2008, the global submarine cable network was severely impacted by a series of cable cuts off the coast of Egypt, which caused widespread outages and highlighted the vulnerability of the infrastructure. Africa was hit particularly hard by these disruptions, as many of its countries depended on a limited number of cables for international connectivity.
Furthermore, geopolitical risks and conflicts in the regions where cables land can also threaten the resilience of submarine cable infrastructure. Political instability, civil unrest, and security risks near cable landing stations can impede maintenance activities and disrupt connectivity. In some cases, tensions between countries have led to concerns about the security of submarine cables, with nations worrying that critical infrastructure might be targeted in the event of a conflict.
Finally, climate change poses an emerging risk to the resilience of submarine cables. Rising sea levels, increased storm activity, and changing ocean currents could affect the integrity of cables laid on the ocean floor. As global warming accelerates, it is crucial to consider the long-term impact of environmental changes on submarine cable infrastructure.
Strengthening Submarine Cable Resilience
To ensure Africa’s digital future is protected, it is essential to prioritize the resilience of submarine cable infrastructure. This requires a multi-faceted approach involving technological, policy, and collaborative solutions.
- Advanced Technology for Cable Protection
Investing in technology to improve the durability and protection of submarine cables is key to mitigating risks. Advances in cable design, including the use of more durable materials, can help safeguard cables from damage caused by fishing activities, anchor dragging, and other human-induced factors. For example, cables with reinforced armoring, which are more resistant to physical stress, can help reduce the impact of these risks.
Additionally, innovative monitoring and early detection systems can be deployed to identify cable faults as soon as they occur. These systems use real-time data to detect changes in the cable’s physical properties, allowing for quicker intervention and repairs before significant damage happens.
Another potential solution lies in the development of more resilient cable routes. By strategically planning cable routes that avoid areas prone to natural hazards or geopolitical tensions, the risk of cable damage can be minimized. For instance, cables could be laid in deeper waters or along less trafficked shipping lanes, where the risk of physical damage is lower.
- Diversification of Connectivity Routes
Given the importance of submarine cables to Africa’s digital economy, diversification of cable routes is critical to ensuring resilience. Over-reliance on a few cables or routes exposes the continent to significant risks, as any disruption to a single cable can cause widespread outages. By investing in more diverse cable systems and improving interconnections, Africa can ensure a more stable and reliable internet connection.
The establishment of redundant cables, which provide backup routes in case of failure, is crucial. Multiple cable routes linking different parts of Africa to the global network can reduce the impact of any single point of failure. Projects like the 2Africa cable, which connects 33 countries in Africa, Europe, and the Middle East, are important steps in creating a more resilient network.
- Collaboration Among Stakeholders
The resilience of submarine cables depends not only on technological advancements but also on the collaboration between governments, businesses, and international organizations. Governments must create favorable regulatory environments that encourage investment in cable infrastructure while making sure that public policies support the development of redundant, secure, and resilient networks.
Public-private partnerships (PPPs) are key to improving submarine cable resilience in Africa. By working together, governments and private telecom operators can pool resources, share expertise, and align strategies to improve infrastructure and respond more effectively to disruptions. For example, regional collaborations such as the African Union’s efforts to build a unified digital market could help strengthen the collective resilience of the continent’s submarine cable systems.
- Investing in Maintenance and Upgrades
Submarine cables require continuous maintenance and periodic upgrades to ensure their reliability. Regular maintenance activities, such as cable repairs, inspections, and equipment upgrades, must be prioritized to prevent long-term service interruptions. In addition, new cable systems should be designed with scalability in mind, securing their ability to accommodate growing bandwidth demands as the continent’s digital economy expands.
Maintaining a skilled workforce capable of handling these tasks is also essential. Investing in training local technicians and engineers will help guarantee that Africa has the human capital needed to address infrastructure challenges and maintain its digital networks.
Towards a Resilient Future
As Africa continues to develop its digital economy, safeguarding the continent’s submarine cable infrastructure is paramount. Submarine cables are the backbone of the continent’s connectivity and digital transformation, and their resilience is key to unlocking opportunities for growth, innovation, and improved quality of life.
By leveraging advanced technologies, diversifying connectivity routes, encouraging collaboration, and investing in ongoing maintenance, Africa can build a more resilient digital future. Submarine cables will continue to play an indispensable role in bridging the digital divide and connecting the continent to the global economy. The success of these efforts will ultimately depend on the continent’s ability to proactively address challenges and safeguard the infrastructure that underpins its digital future.